What Happens When You Don't
Have Enough
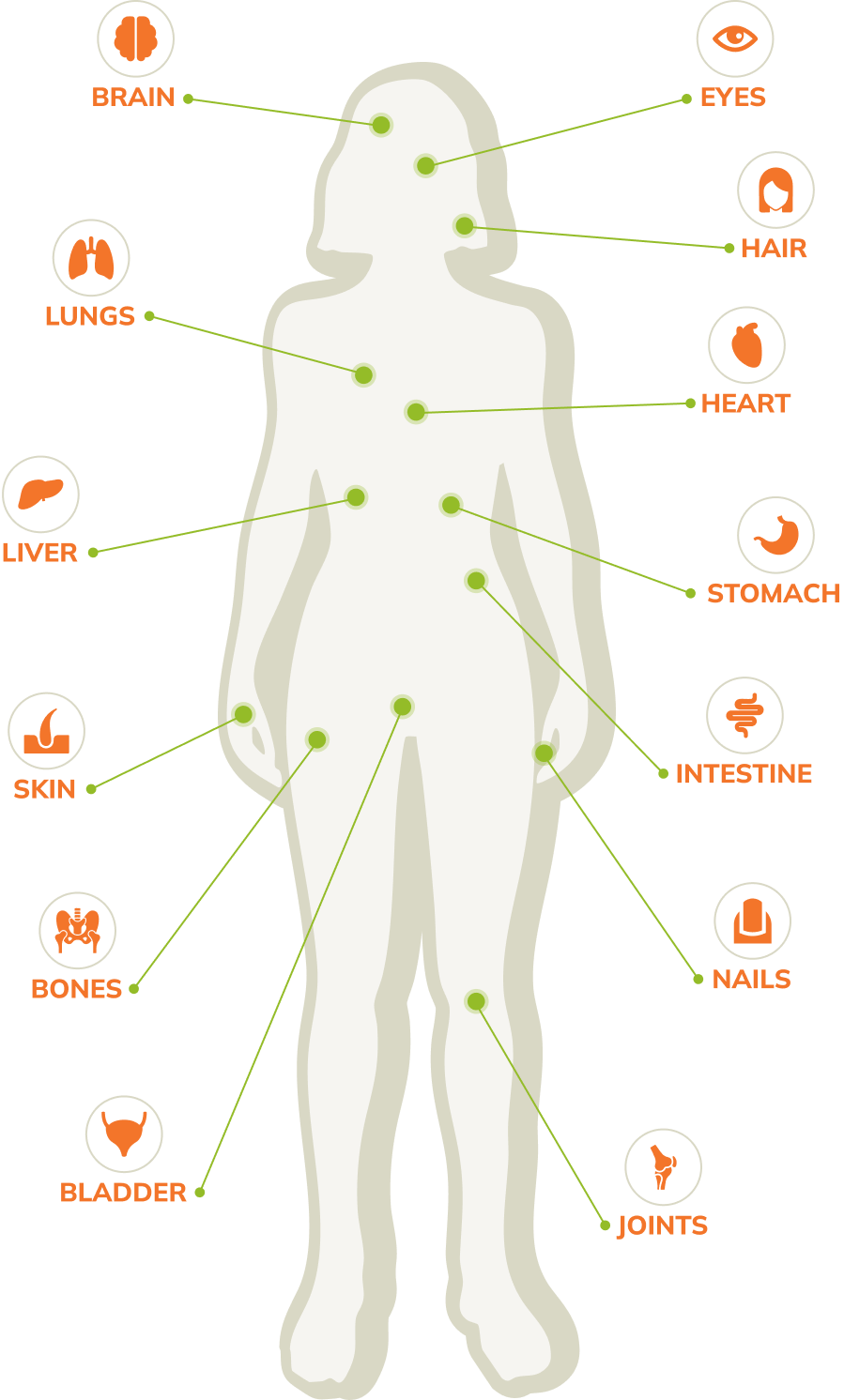
Unfortunately, this rationing in the face of nutrient deficiencies can lead to dire consequences. For instance, when there is a chronic deficiency in vitamin K the body produces fewer enzymes required for keeping the arteries clear of calcium deposits, which has been linked to higher rates of mortality from cardiovascular disease.
“Because nutrient deficiencies are highly prevalent in the United States and elsewhere, appropriate supplementation and/or an improved diet could reduce much of the consequent risk of chronic disease and premature aging," Ames said.
So Many People are Nutrient Deficient Which Leads to Health Problems
Using as a reference the estimated average requirement (EAR) value, the level which is adequate for half of the population and inadequate for the other half, Ames said research shows as many as 70 percent of Americans are deficient in one or more key nutrients. The numbers he cites in terms of deficiency for known vitamins is: vitamin D, 70%; vitamin E, 60%; magnesium, 45%; calcium, 38%; vitamin K, 35%; vitamin A, 34%; vitamin C, 25%; zinc, 8%; vitamin B6, 8%; folate, 8%.
And that's just the vitamins and minerals which have been classified as such and for which a level has been established. The other nutrients that have not yet been classified as vitamins are not as common and their intake is likely much lower.
“Diet is very important for our long-term health and this theoretical framework just reinforces that you should try to do what your mother told you: eat your veggies, eat your fruit, give up sugary soft drinks and empty carbohydrates,” Ames said.